Get the point! | What is Scan to BIM and How it is helping the AEC Industry
The AEC industry is undergoing a digital revolution. Tasks like heritage on-site documentation are leveraging new technologies, such as BIM. Digitally replicating a structure in BIM gives a precise output, but the documentation process takes time.
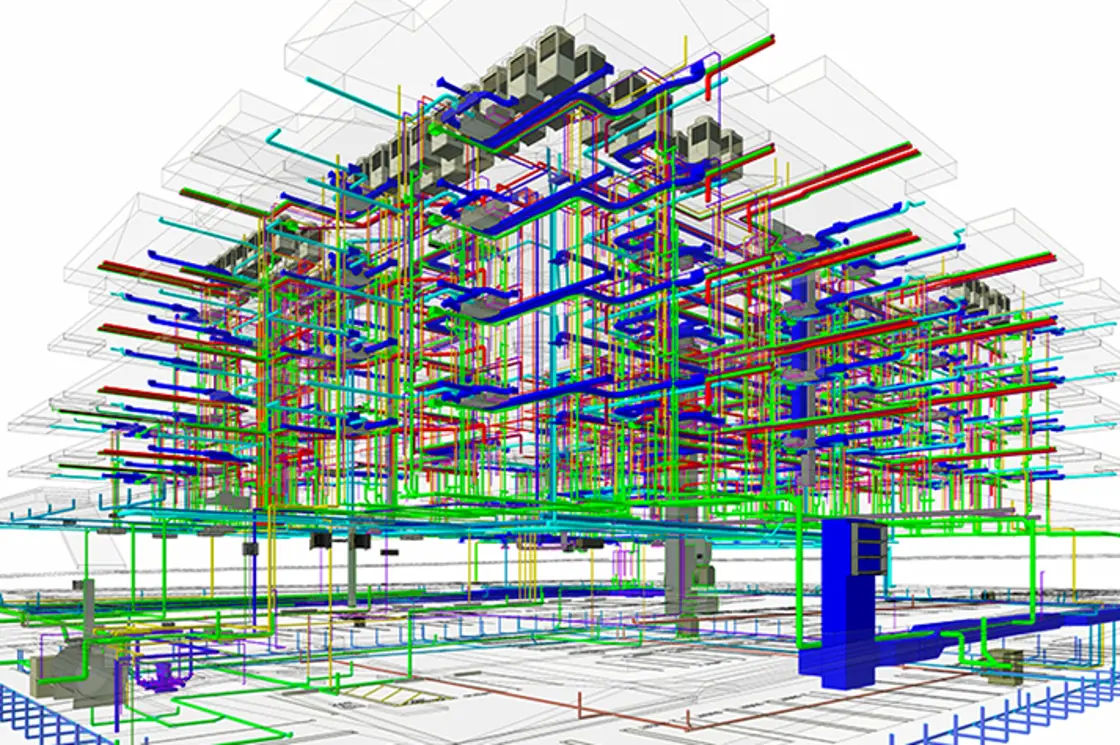
Enter Scan to BIM – a convenient and efficient way to document on-site conditions. Scan to BIM utilizes 3D laser scanning to record building information as point-cloud data. This data forms the basis for creating “as-is” BIM models. Architects in countries like the UK and the US are using Scan to BIM, especially in the restoration of old monuments.
What is this laser scanning process? Is it accurate? How do we decipher the point cloud to create accurate 3D Models?
Let’s find out.
Why Scan?
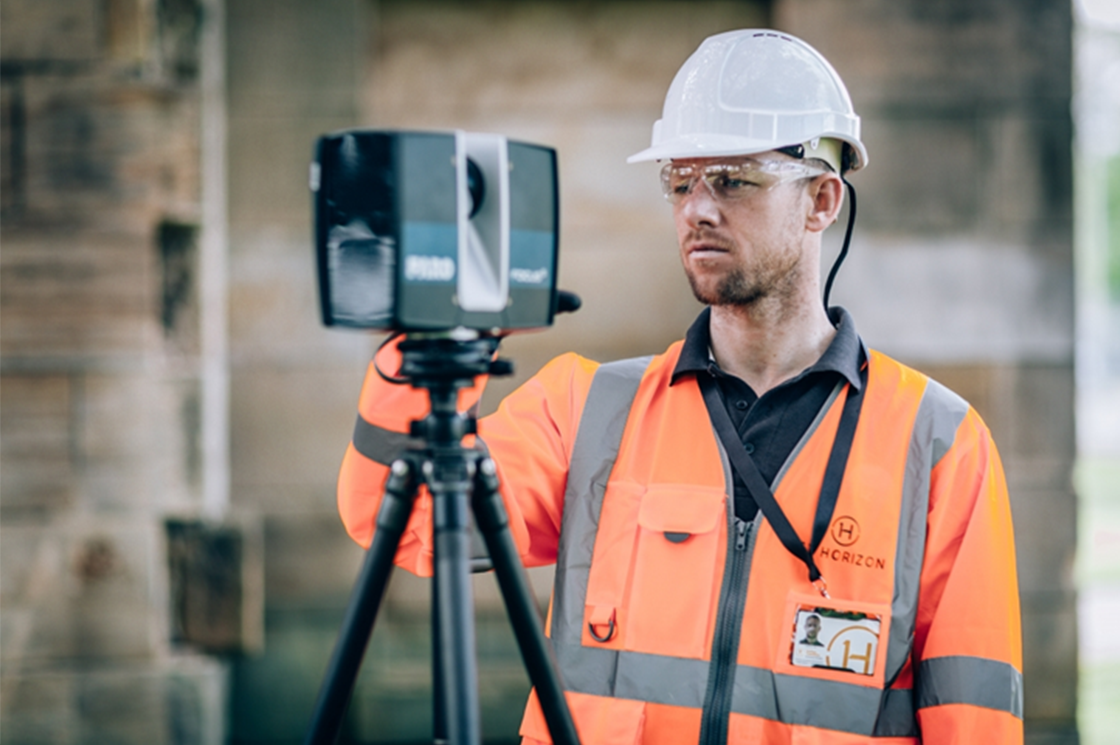

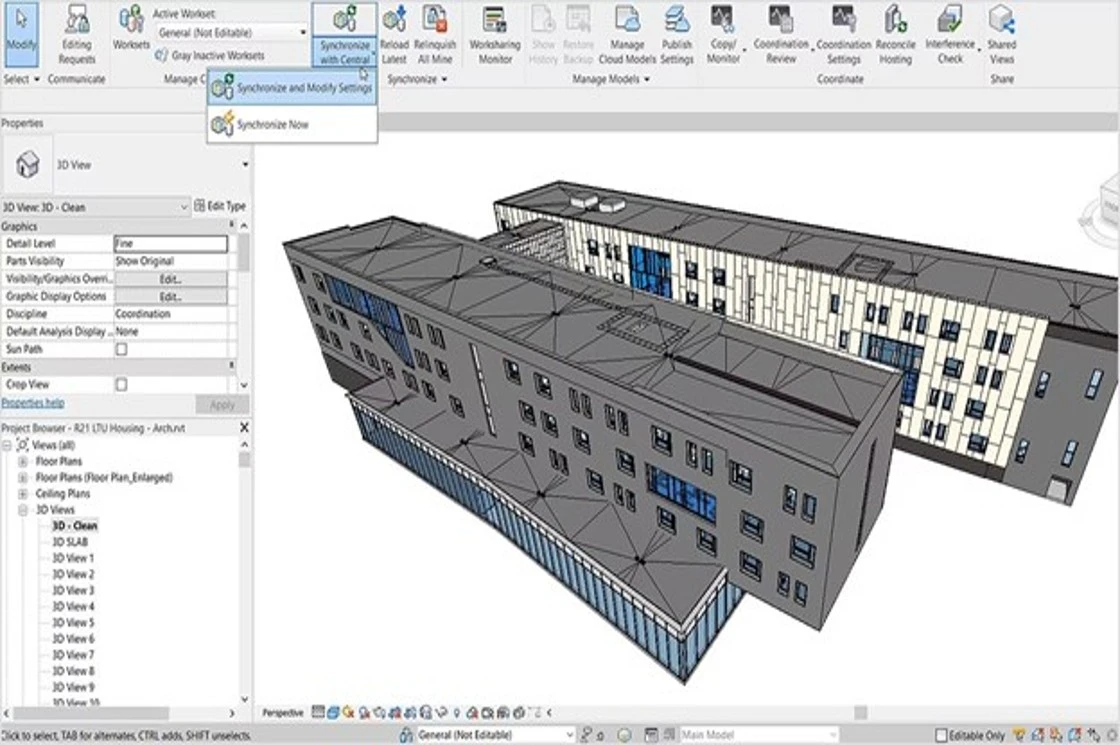
Laser scanning was introduced around the 1990s and soon integrated with BIM tools such as Autodesk Revit through Scan to BIM.
This process is quick and efficient, especially for renovation or restoration projects. The accuracy and precision of the outcome are dependent on the technology and efficiency of the scanning process.
What is Point Cloud?
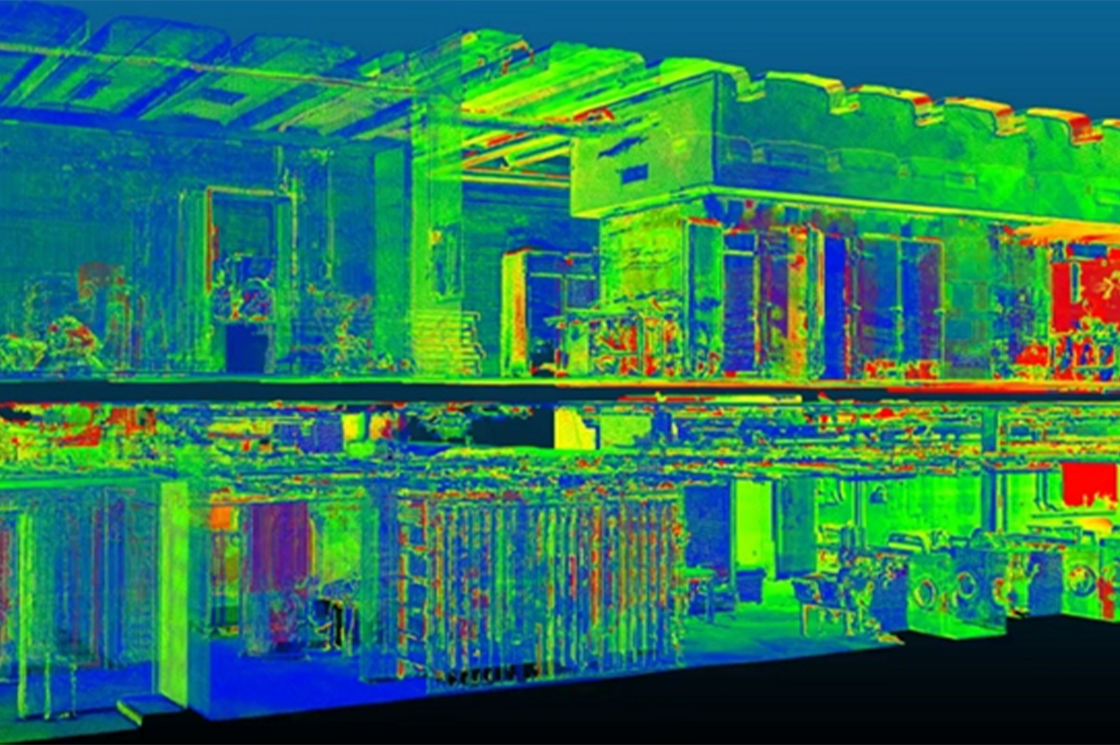
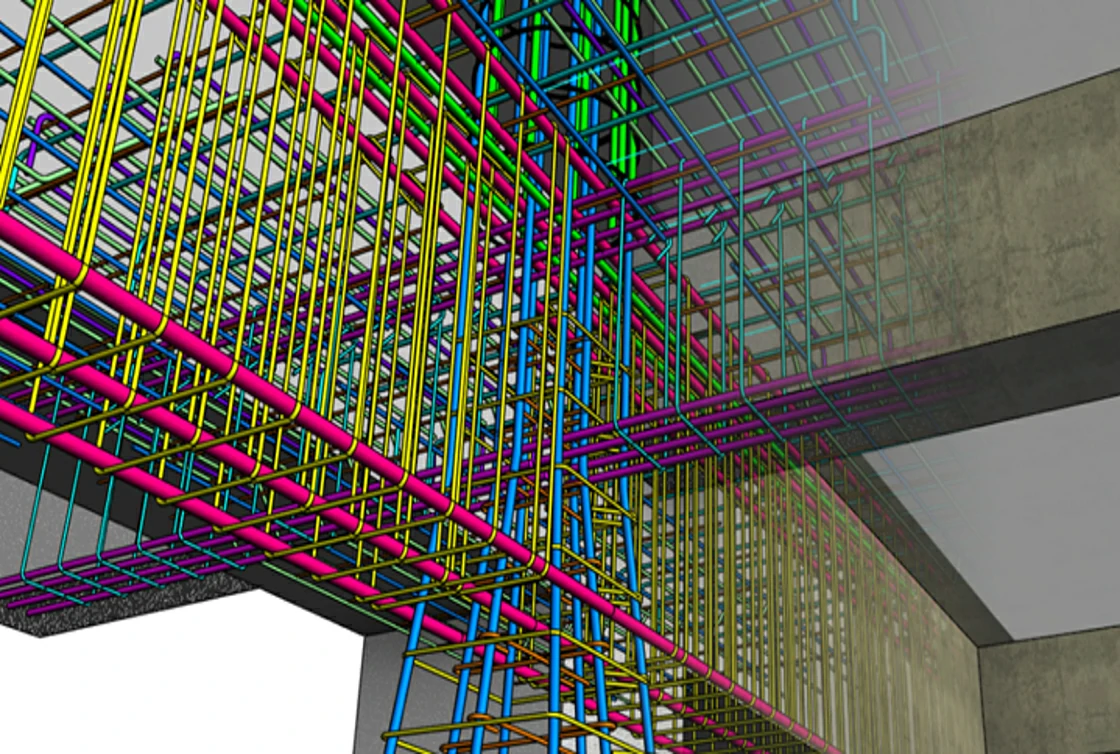
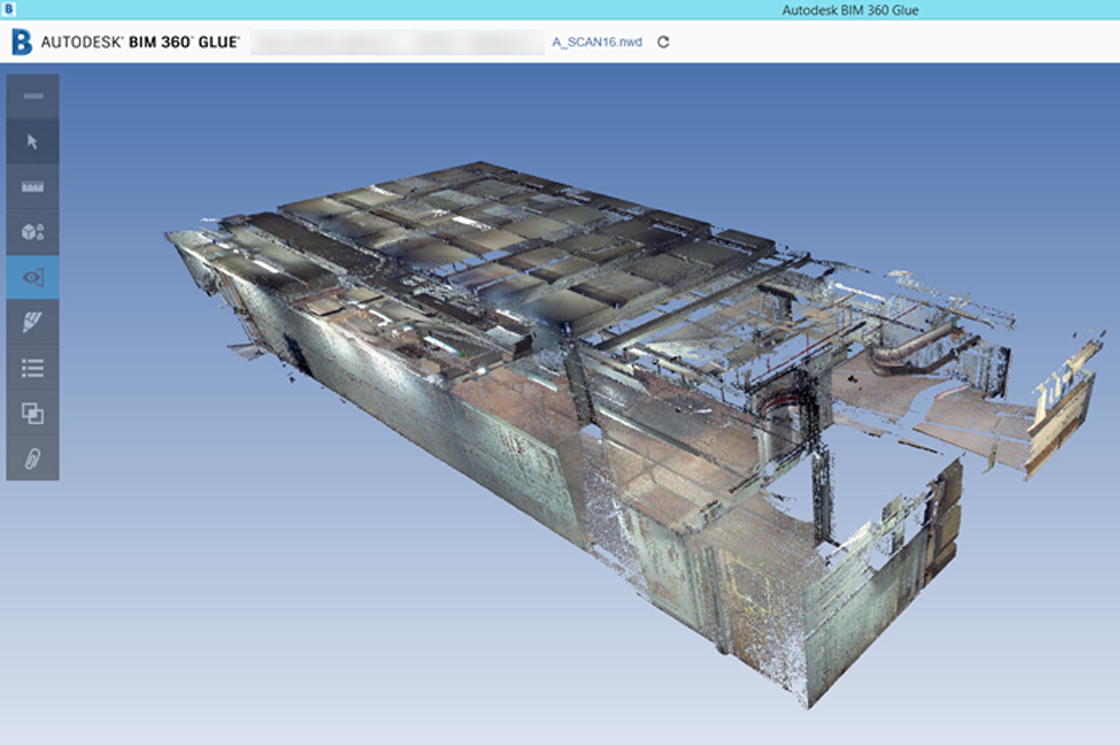
The 3D laser scanner captures the geometric information of a building as point clouds. A point cloud is a set of points of a 3D shape or object in space. It is used to create 3D CAD models for manufacturing, quality inspection, visualization, and rendering.
All objects can be understood as existing in a 3D space which can be defined by the three cardinal axes – x, y, and z. Hence, their geometric configuration can be coded through a set of point coordinates. Laser scanners record these coordinate points as point clouds in digital 3D spaces.
7 ‘Points’ of Scan to BIM
Like all great technology, Scan to BIM can only be leveraged to your advantage if you plan the process and optimize the workflow. The process can be understood as seven simple steps:
Step 1: Set Goal
Laser scanning produces an enormous amount of data. Moreover, the record of this data is limited by the line-of-sight of the scanner. It is hence crucial to define the scope and purpose of the scan, to obtain all the information with the minimum number of scans.
Step 2: Assign Responsibilities
It is crucial that everyone on the team understand their role in the process beforehand. Knowing who is going to scan, verify and interpret the data helps with efficient planning and execution.
Step 3: Set the Scanner
Once everything is planned, the scanner is set up and the parameters are fed to it, such as the point-cloud density, etc.
Step 4: Scan, Scan, Scan!
A complete representation of the building usually demands more than one scan, as the information is limited to the line of sight of the scanner. Hence, multiple scans need to be pre-planned in order to utilize the technology efficiently.
Step 5: Transfer Data
The data that is recorded (point cloud) is then transferred to a computer using a USB drive or a cloud platform.
Step 6: Into the Point Cloud
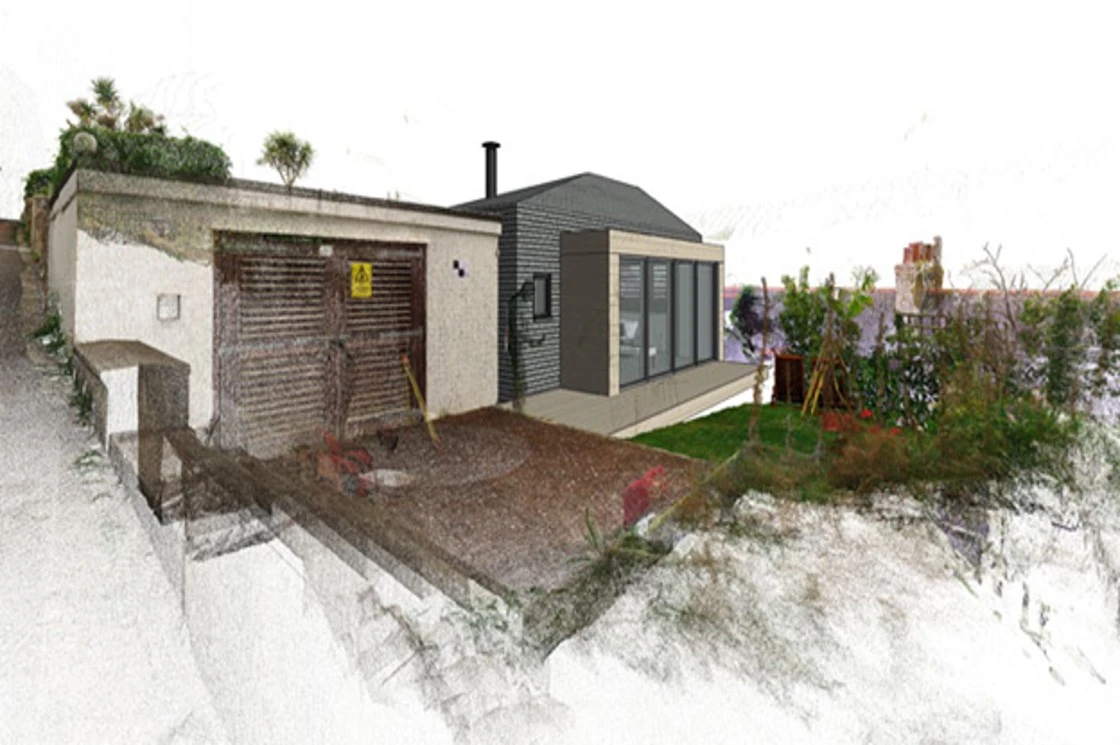
The scan data needs to be composed together into a single point cloud representing the entire structure. Point cloud modeling software such as ReCap Pro is used to register, analyze and model such data.
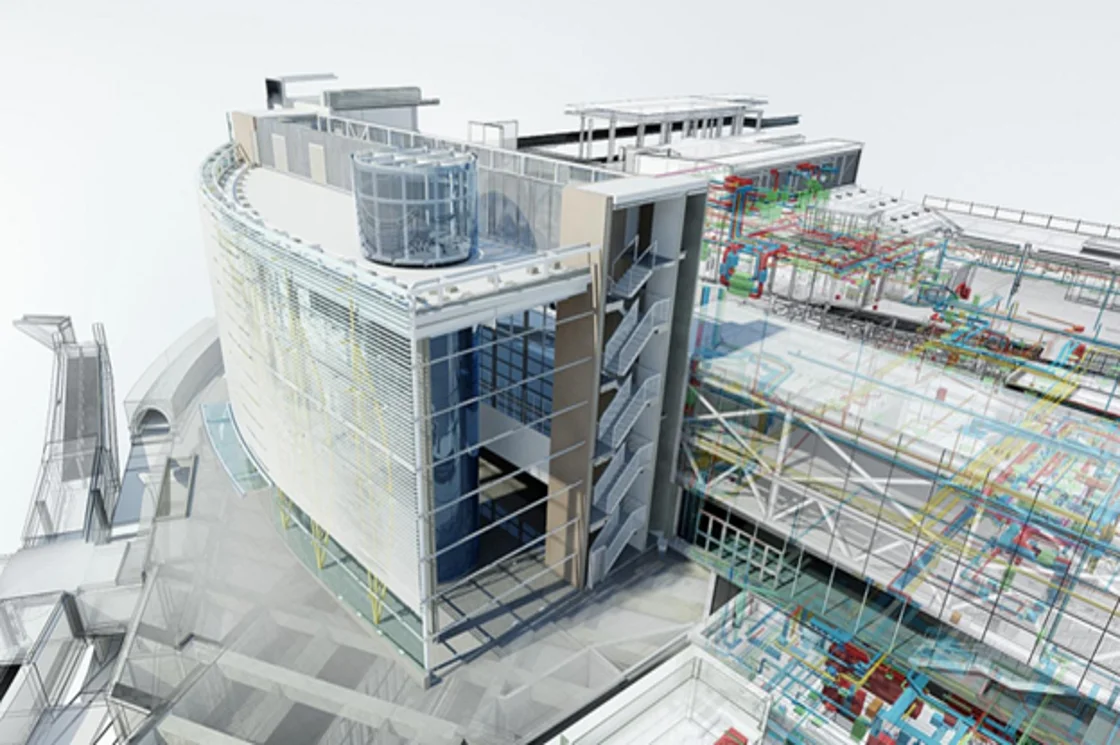
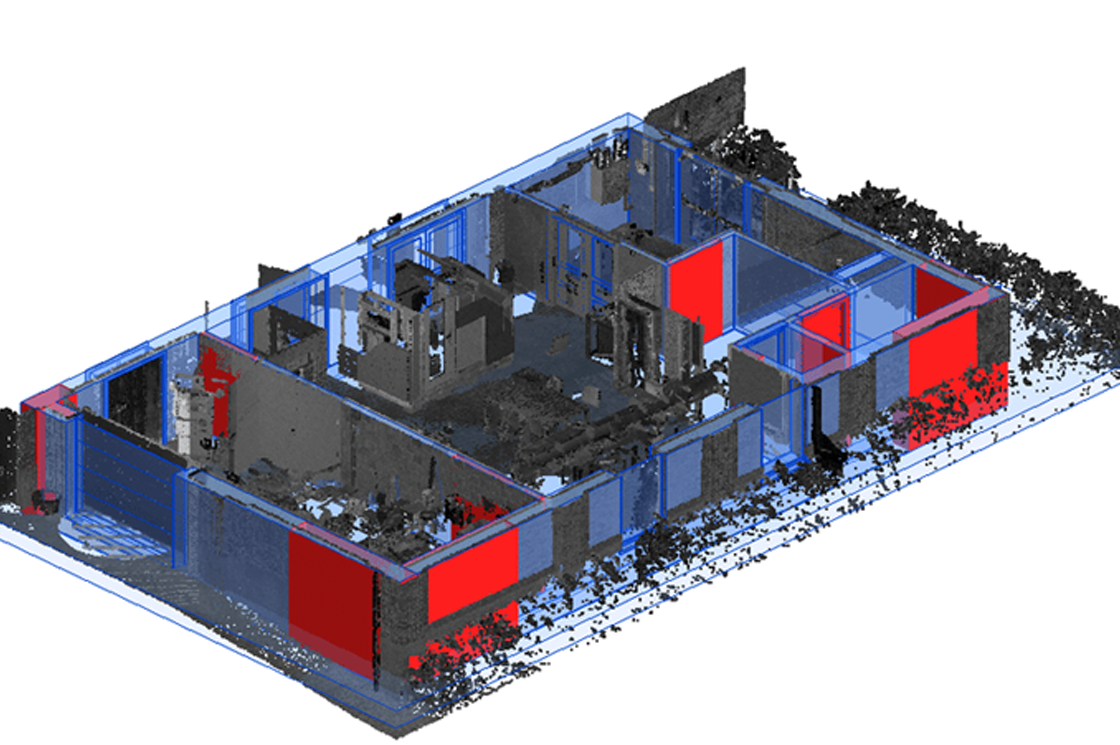
From Point Cloud to BIM
Congratulations, you have Scanned to BIM! The point cloud can now be used to create a 3D model using BIM tools such as Revit.
Applications of Scan to BIM
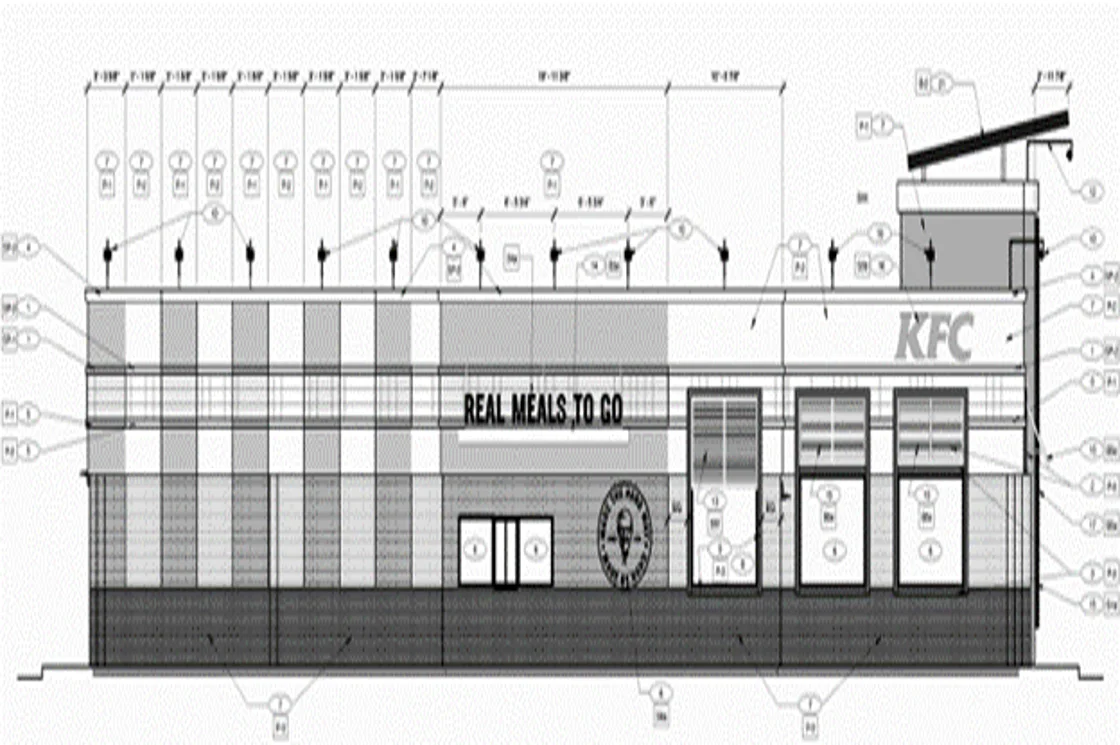
BIM helps in generating and managing the facilities of a building throughout its life-cycle. Scan to BIM, hence, finds applications in many stages of the construction process.
1. Design
Helps in understanding and recording the ‘as-is’ conditions on the site terrain and surroundings. Aids in making design decisions faster.
2. Construction
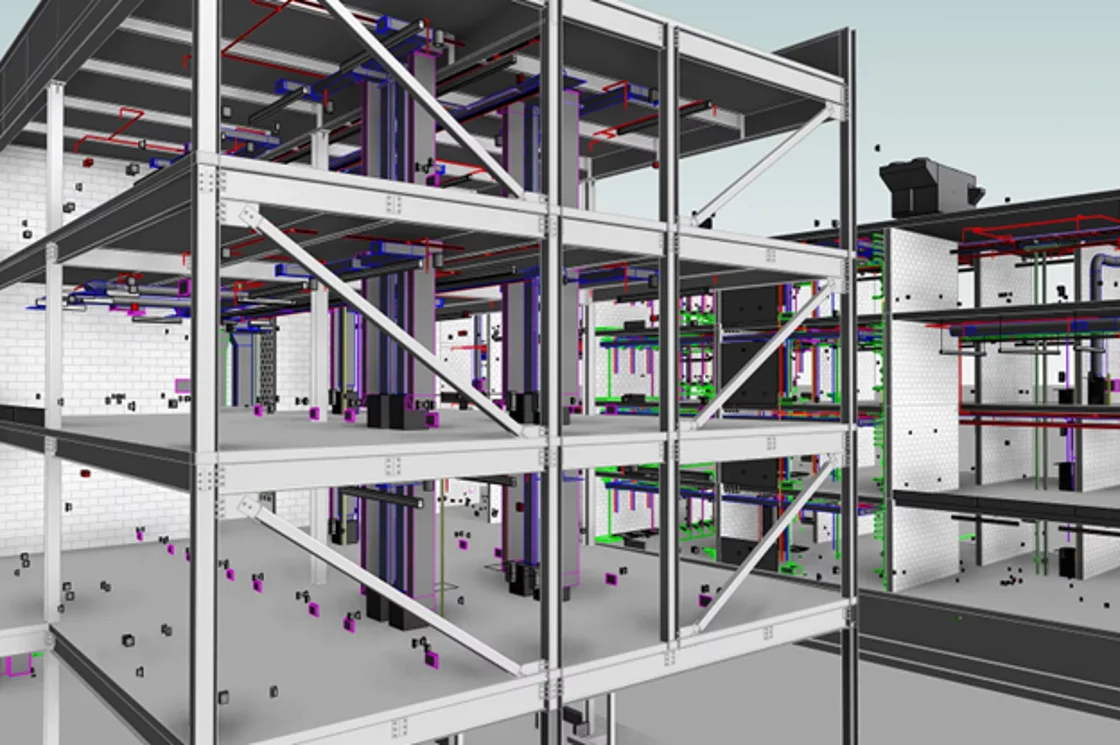
Used for virtual installation and assembly, enhancement of construction safety, digital replication, and quality assurance.
3. Facility Management
Documentation of structures and monuments, building performance analysis, operations management, and space management.
Top 5 Advantages of Scan to BIM
1. Saves Time
Scan to BIM reduces the process of documentation from hours to a matter of minutes. New technologies have automated the journey from Point Cloud to BIM. It also eliminates the need for frequent site visits.
2. Minimal Errors
Decision-making is faster by using Scan to BIM, thus making time for adapting the design to the site conditions and making changes to the project.
3. Quality
Point-Cloud data is usually accurate and precise, serving as a reliable source of information thus leading to quality output.
4. Sustainability
With precise site conditions obtained before designing, planning for it becomes easier. Moreover, laser scanning has minimal interventions to the existing structure.
5. Saves Cost
Compared to the traditional methods of 2D documentation, Scan to BIM results in great cost savings in the long run.
Getting to the Point
Scan to BIM utilizes laser scanning to quickly record existing data as point clouds to create an accurate 3D digital representation. It is getting popular as a means of documentation for its time and cost savings.Scan to BIM is especially useful for documenting heritage buildings as it is the least invasive means to record data.
With its convenience and efficiency,Scan to BIM is leveraging the latest technology to pave the way to an efficient and sustainable world.
FAQs: Scan to BIM
1. Why is Scan to BIM used?
Scan to BIM is used for a range of visualization and animation purposes, mass customization, and digital modeling of fabricated components.
2. How does laser scanning relate to BIM?
Laser Scanning is a part of the Scan to BIM workflow used to transfer real-world conditions into a project.
3. What does BIM stand for?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, a working methodology of creating and managing all building information through one shared digital model.
4. What is Scan to BIM in Revit?
Real-world conditions are captured as point cloud data which is used for the development of a BIM model in Revit.